
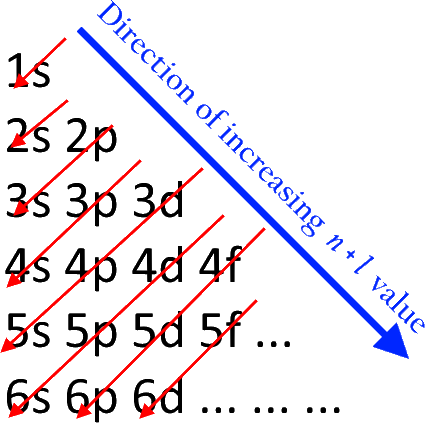
Note: Values of Azimuthal quantum numbers are as follows: s=0, p=1, d=2, f=3.Įlectronic Configuration using the Aufbau Principleįirst electrons are filled in 1s orbital.

In a tabular form, the arrangement of orbitals with increasing energies as per The electronic(n+l) rule can be shown as follows: This diagram is also referred to as the Aufbau principle diagram and is used to remember the order of the filling of the orbitals. Order of filing of orbitals by Aufbau principleġs, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s… The order in which the energies of the electronic orbitals increase and their respective order of filling as per the Aufbau rule is as follows:įigure 1. And, if two orbitals have the same value for (n+l) then the one with a higher value of n will have higher energy.ĭuring filling up of electrons in the orbitals for completion of electronic configuration, electrons will first occupy the orbitals of lower energy only after the lower energy orbitals are occupied, the electrons shall occupy the higher energy orbitals. The lower the value of (n+l) for an orbital, the lower will be its energy. The energy of an orbital is determined by the (n+l) rule where ‘n’ stands for the Principal quantum number and ‘l’ stands for the Azimuthal quantum number. an electron will initially occupy an orbital of lower energy level and when the lower energy level orbitals are occupied, then only they shall start occupying the higher energy level orbitals. In other words, “In a ground state of the atoms, the orbitals are filled in order of their increasing energies." i.e. 'Building up’, as the name suggests, is regarding the filling of the orbitals with electrons to build the electronic configuration in a particular way so that an orbital with lower energy is filled earlier and the orbital with higher energy is filled later. This principle is concerned with the filling of the electrons in an orbital during the writing of an electronic configuration. Aufbau is a German word that means 'building up and is not the name of a scientist unlike many of the other principles of chemistry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
